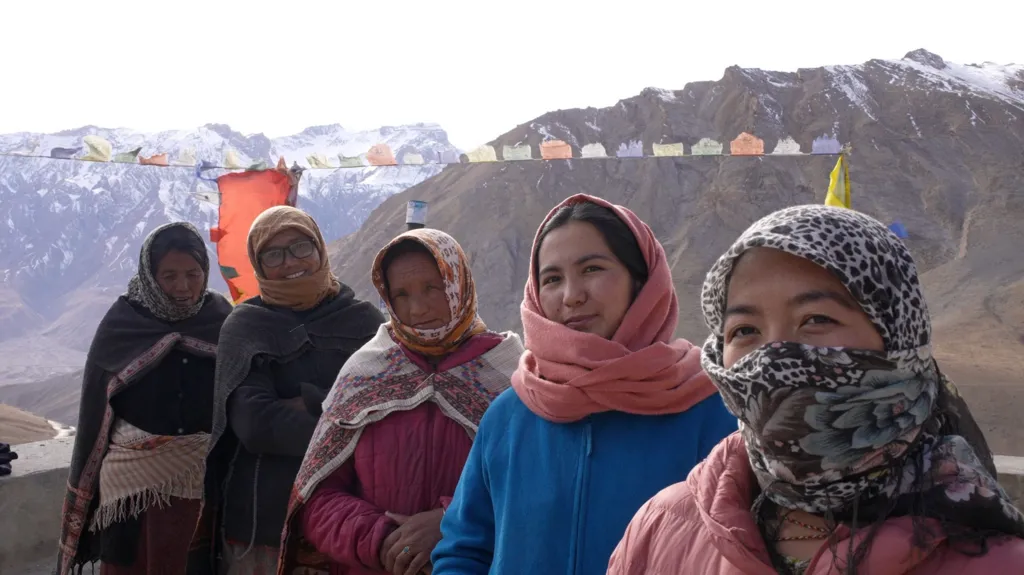
 |
| These women work with the Himachal Pradesh forest department to track and protect snow leopards. |
High in the frozen mountains of Central and South Asia, the snow leopard moves almost unseen. It is the charismatic apex predator of the high snows, perfectly adapted to some of the harshest terrain on Earth. Of the twelve countries where it is found, India is home to one of the world’s largest populations. In 2023, the country completed its first comprehensive national survey, estimating that more than 700 snow leopards survive across its Himalayan and trans-Himalayan landscapes. One of their strongholds lies around the village of Kibber, in Himachal Pradesh’s Spiti Valley—a stark, high-altitude cold desert carved into the Himalayan belt. For generations, the snow leopard was regarded here chiefly as a threat to livestock and livelihoods. Now, in Kibber and nearby villages, attitudes are beginning to shift, as communities come to see the animal not as an adversary, but as a vital presence in a fragile mountain ecosystem. One group of women has gone a step further, placing themselves at the centre of efforts to protect it.
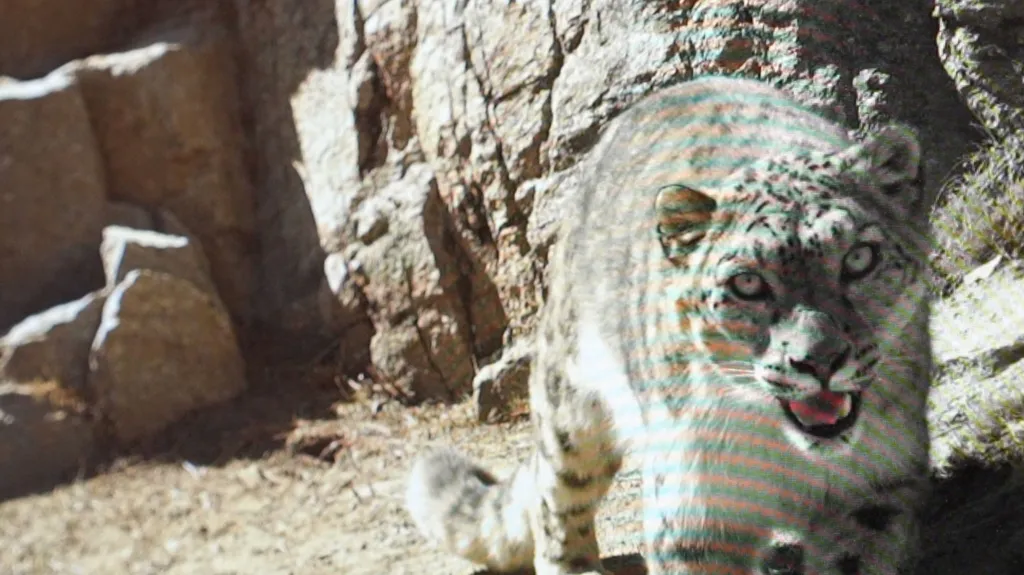 |
| A snow leopard captured on camera trap. |
They call themselves Shenmo, taking their name from the local word for the snow leopard—shen. The group is made up of nearly a dozen women who work alongside Himachal Pradesh’s forest department and conservation scientists to monitor and safeguard the cats. Trained to install and maintain camera traps fitted with unique identification codes and memory cards, they help capture fleeting images of wildlife as it passes silently through the mountains. Among them is Lobzang Yangchen, a local coordinator working with a small community group supported by the Nature Conservation Foundation (NCF) in partnership with the forest department. She was part of the team that contributed data to Himachal Pradesh’s snow leopard survey in 2024, which recorded 83 snow leopards in the state—up from 51 just three years earlier. Spread across nearly 10,000 square miles, the camera traps also documented 43 other species. Individual snow leopards were identified by the distinctive rosette patterns on their fur, and the findings are now shaping wider conservation and habitat management plans.
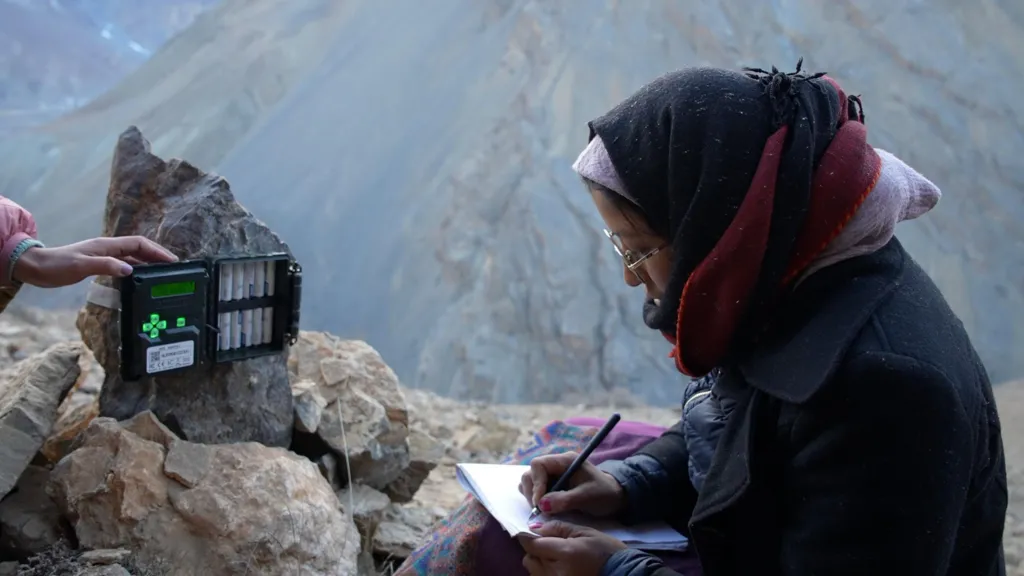 |
| One of the women recording data from a camera trap. |
Much of this work takes place in winter, when heavy snowfall pushes snow leopards and their prey down to lower elevations, revealing tracks that would otherwise remain hidden. For the women of Shenmo, a survey day begins after household chores are finished. They gather at a base camp and travel by vehicle for as long as the terrain allows, before continuing on foot—often hiking several kilometres to camera sites more than 14,000 feet above sea level. One such trek in December was accompanied by the BBC. Along a narrow mountain trail, the women paused where fresh pugmarks marked the snow. They searched for other signs—scrapes and scent-marking spots—before carefully fixing a camera to a rock overlooking the path. To test the setup, one woman carried out a “walk test,” crawling along the trail to ensure the camera’s height and angle would capture a clear image. Later, they visited older camera sites to retrieve memory cards and replace batteries installed weeks earlier. By mid-afternoon, the team returned to camp to log and analyse the images using specialised software.
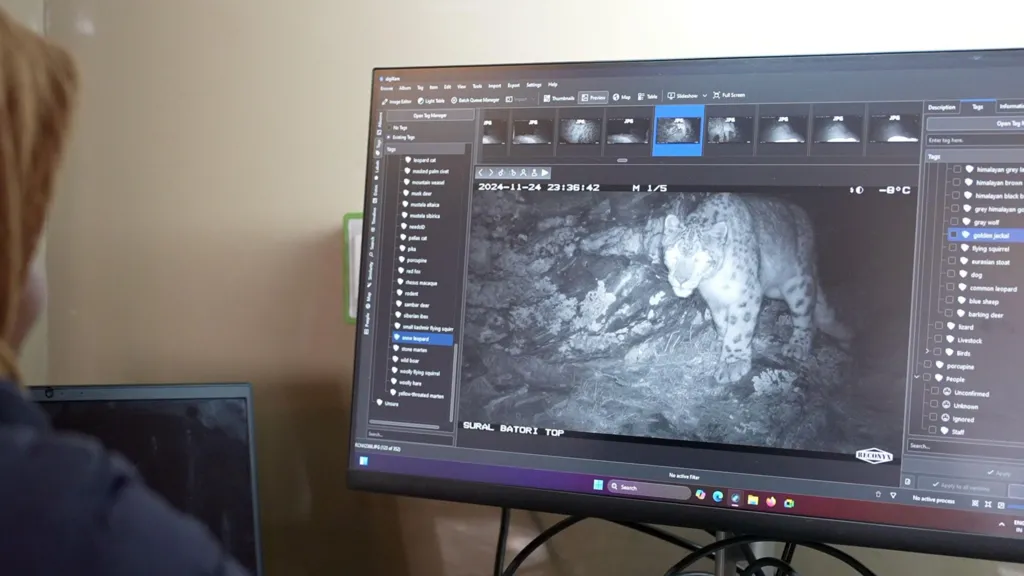 |
| Snow leopard images captured by camera traps being analyzed. |
The women who joined the camera-trapping programme in 2023 did not set out to become conservationists. In Spiti Valley, winter is long and unforgiving, a season when fields lie dormant and work is scarce. With little agricultural labour to fall back on, curiosity—and the chance to earn a small daily wage—drew them in. As Lobzang Yangchen recalls, the income of 500 to 700 rupees a day mattered. What none of them anticipated was how this work would slowly alter not only their own perspectives, but the way their community viewed the snow leopard. Over time, their role expanded beyond tracking wildlife. The women now help villagers navigate government insurance schemes to offset livestock losses, and encourage the use of predator-proof corrals made of stone or wire mesh to keep animals safe through the night. Their efforts coincide with a growing recognition of the region’s ecological importance. Spiti Valley has recently been included in the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO-recognized landscape designed to protect fragile ecosystems while sustaining the people who live within them. As climate change reshapes the trans-Himalayan plateau, conservationists say such local partnerships are no longer optional—they are essential. Deepshikha Sharma, program manager with the NCF’s High Altitudes initiative, describes the women of Shenmo not as volunteers, but as practitioners—active participants in wildlife monitoring and protection. For the women themselves, the work carries a simpler meaning. It brings them closer to the land they have always called home.
Their story, however, does not stand alone. Thousands of kilometers away, in the dense mangrove forests of the Sundarbans, women who have lost their husbands to tiger attacks are restoring damaged coastlines by planting mangrove saplings—natural defences against cyclones that are becoming more intense as the climate warms. From the frozen slopes of Spiti to the shifting delta of eastern India, local women are emerging as unexpected guardians of some of the country’s most fragile environments. Through quiet, persistent effort, they are showing that conservation does not begin in distant institutions, but in the daily lives of those who live closest to the wild.














